Definition of Painting Style
The painting style is a distinctive style, genre, or understanding that is followed by certain individuals or groups in creating works of painting. The style in question can be in the form of the main idea that was sparked by someone, or a natural flow that appears by itself in line with the development of painting.
It should also be noted that some of the Styles usually have a dialogue with each other. For example, Style B arises because they feel that Style A is no longer relevant to the conditions of the times, or to corner certain people, Style C arises because they feel that both are perfect when combined.
The style or school of painting is also always influenced or can be said to be shaped by the state of society at a time. There are big Styles that have an equally strong influence, there are also minor Styles that don’t get as much attention. In the past, the style of naturalism and realism was the most influential, because it had an applicative function as documentation before the camera replaced it. Today, the style is still surviving but not as strong as before.
Many lessons, inspiration, and knowledge can be drawn from the various styles of painting that exist. Therefore, learning the style of painting will open up many new treasures, either just to appreciate it better, or to engage in the world of painting. The following are some of the greatest painting styles in order of their appearance.
The Greatest & Most Important Painting Style in History
Romanticism
Romanticism style is a style that depicts a reality that exists more dramatically and has a dream-like atmosphere. Ships bobbing in stormy weather, Human figures standing on top of hills at dusk, etc. Romanticism reveals the beauty of a theme from its theatrical style, not just relying on beautiful subjects.
Example of Romanticism Style

The Characteristics of Romanticism Style
- Imaginative; While still realistic (no fantasy), the scenes seem more dramatic than reality.
- Subjective; The creation of art is considered as an artist’s self-expression.
- Using high emotional intensity.
- The image or atmosphere has a dream-like quality (like a dream).
- Describe strong feelings that are not literal or use imagery and symbols.
Important figures of Romanticism
- Francisco Goya
- Caspar David Friedrich
- JMW Turner
- Theodore Gericault
- Henry Fuseli
- Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres
Naturalism
Naturalism style is a style that wants to depict nature as closely and accurately as possible according to the reference it paints. Naturalism is an opportunity for artists to appreciate nature. Artists will usually choose a certain time of day (twilight/golden hour) to paint an extraordinary scene.

Characteristics of Naturalism Painting Style
- Prioritizing the similarity of the image in the painting with the object painted according to the reference
- The artist’s technique and expertise are the main weapons
- Bringing beautiful painting themes but based on purity
- Naturalism is an artist’s form of appreciation for the beauty of nature
- Raising the theme of the beauty of the scenery around the artist
The figure of Naturalism Painting Style
- John Constable
- Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot
- Theodore Rousseau
- Thomas Cole
- Frederic Edwin Church
- Ilya Repin
- Basuki Abdullah
Realism
Realism is a style that wants to display an event, atmosphere, or a certain model with everyday situations, without being dramatized or choosing the most beautiful situation. This style may not copy perfectly what it sees, the events or themes are realistic, not just the pictures.

Characteristics of Realism Painting Style
- Lifting the daily events experienced by most people
- Describing people in real and typical situations with their daily environment
- Realist works depict humans from all classes in their original situations and conditions.
- Realism does not agree with the subject of art that is exaggerated (dramatic) in the style of Romanticism.
- Has a detailed image that resembles the original (natural) through high techniques mastered by the painter.
Realism Painting Style Figure
- Gustave Courbet
- Jean-Francois millet
- Edouard Manet
- James Whistler
- John Singer Sargent
- Thomas Eakins
Impressionism
Impressionism is a style of painting that only paints a fleeting impression of the subject being painted. This style arose because of the presence of a camera that had taken over the function of art as a documentation medium. Rather than replicating colors as humans see them, Impressionism wants to describe pure colors based on the process by which color is formed.
Usually, the Impressionists painted outdoors for a short period, so they had to sacrifice the accuracy of form, which is the reason why their paintings are usually only impressions. They didn’t have time to work out any further details. However, from these imperfections, a new aesthetic form emerged that was not owned by realism, naturalism, and event photography.
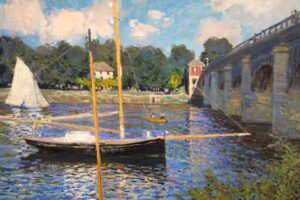
Characteristics of Impressionist Painting Style
- The picture on the painting is not detailed, the painting only looks similar when viewed from a distance
- Bright and contrasting color palette based on color circle grouping theory
- Focus on painting the reflection of light on the subject, not the subject itself
- Using a brush technique called dab which is an external term for dipping sambal
- Don’t use black
Impressionist Painting Style Figures
- Claude Monet
- Edgar Degas
- Pierre-Auguste Renoir
- Camille Pissarro
- Alfred Sisley
Fauvism
Fauvism uses a style that is almost similar to Impressionism but rejects the basic idea, namely: imitation of nature. Fauvism style makes color an independent element of art. Color is not only the color of clothes, the color of the sky, or the color of the skin but becomes one of the elements that stand alone without being any physical representation.

Features of Fauvism Painting Style
- Striking colors that do not see the accuracy of the reference model being painted.
- The shape of the image in the painting is accompanied by dark solid lines
- Color is used to express an Artist’s idea, not just a colorant
- The accuracy of the details of the shape of the image on the reference model or subject is ignored
- Convey an idea or a personal message from the artist
Fauvism figures
- Henri Matisse
- Maurice de Vlaminck
- Andre Derain
- Kees van Dongen
- Raoul Dufy
- Georges Braque
Expressionism
Expressionism is a style that prioritizes the artist’s expression of what he remembers, sees, and feels. It can be said that expressionism is an art style that emphasizes expression from within the soul. Expressionism will not impose the precision and difficulty of painting on his work. Therefore, this style does not have an accurate level of resemblance and even deviates from natural references.
Characteristics of Expressionism Painting Style
- Not prioritizing the resemblance of the object being painted
- Bold and expressive brush strokes (brush marks are left exposed and not hidden)
- Drawing technique that looks naive (amateur) but still has good composition
- Emphasizes the expression of the artist’s soul compared to copying nature
- Using color as a symbol for something, not just an object coloring
Figure of Expressionism
- Ernst Ludwig Kirchner
- Wassily Kandinsky
- Kathe Kollwitz
- Paul Klee
- Chaim Soutine
- Max Beckmann
Cubism
Cubism is a style that includes several points of view of an object in the same image, resulting in a fragmented and deformed painting. This style also simplifies objects to resemble geometric shapes. An object of painting can consist of various angles simultaneously to produce an aesthetic clumsiness.

Cubism Characteristics
- Use multiple perspectives at once in one image.
- Deformation and deconstruction of the object being painted, such as the position of the mouth being confused with the position of the nose
- Simplify objects to resemble geometric shapes
- Explore open shapes and blend the background with the object in front of it.
- In the second phase of Cubism, many used everyday objects as collages (newspaper pieces, etc.).
Cubism figures
- Pablo Picasso
- Georges Braque
- Fernand Leger
- Juan Gris
- Robert Delaunay
- Sonia Delaunay
Dadaism
Dadaism is a style that does not make a physically beautiful work but contains sharp criticism or social messages by making indirect satire, to direct provocative expressions against the authorities who are considered to have made negative decisions.
Dadaism style exudes aesthetic beauty from sides that are rarely contained in generic or ordinary beauty, such as beauty in irregularity and something random but still balanced.

Characteristics of the Dadaist Style
- Displays a picture that is not beautiful and provocative.
- Contains messages that question the meaning of art, the role of artists, and aesthetics in general.
- Delivering anti-war appeals through satire or satire on the atrocities of war.
- Contains messages against the bourgeoisie which at that time was considered to have caused World War I
- Using “readymade” objects or something that already exists, such as everyday objects such as glasses, toilets, spoons, etc.
Dadaist
- Francis Picabia
- Marcel Duchamp
- Man Ray
- Hannah Hoch
- Sophie Taeuber-Arp
- Andre Breton
Surrealism
Surrealism is a style that presents images of real objects in situations that are not possible in the real world so that the image is like in a dream. Pictures that are real but in an unreal state are like: A floating human, a melted wall clock, or a portrait of a face with a nose and mouth that is in different positions.
Surrealism uses Freud’s psychological theory approach which explores the subconscious and the image of human dreams as a depiction of human desires.

Characteristics of Surrealism Painting Style
- Loading images of real objects in an unreal state
- Imaging like in a dream
- Has high contrast, in the sense: there is a large shape next to a small shape
- Playing the images contained in dreams with the real world
- Looks like fantasy but sticks to real-world references
The figure of Surrealism Painting Style
- Salvador Dali
- Andre Breton
- Hans Arp
- Max Ernst
- Alberto Giacometti
- Joan Miro






Leave a Reply